I. Laminoplasty
A surgical procedure for cervical spinal cord decompression, indicated for multi-level spinal canal stenosis. The procedure involves cutting the lamina unilaterally or bilaterally, allowing it to be shifted posterolaterally to expand the spinal canal. This increases the space for the spinal cord, thus relieving compression, promoting spinal cord healing, and alleviating symptoms.

II. Advantages of Vertebroplasty
· Preserves segmental mobility.
· Avoids fusion-related complications (Adjacent Segment Degeneration/Disease (ASD), pseudoarthrosis, etc.).
· Prevents kyphotic deformity.
· Prevents epidural scar formation.
· Preservation of the lamina provides posterior protection for the spinal cord: against injury, paralysis.
III. Development of Laminoplasty
Laminoplasty was developed by Japanese orthopedic surgeons in the 1970s. The earliest laminoplasty involved cutting the lamina in a Z-shape; Oyama termed this method Z-shaped laminoplasty (Z-laminoplasty). In 1977, Hirabayashi and his colleagues developed the open-door laminoplasty, which used sutures to hold the opened lamina flap. Later, Kurokawa and his team developed the French-door laminoplasty (double-door laminoplasty). This procedure involves a midline cut and creating hinges on both sides.
Subsequent refinements to these surgical techniques evolved into methods utilizing miniplates and screws in a "crossbeam" bridging configuration. This secures the elevated lamina directly to the lateral mass, achieving immediate and stable fixation. Several companies currently offer such titanium plates on the market, such as the Centerpiece plate, Arch plate, and Mainstay plate.
The above products all utilize conventional surgical procedures during operation. That is, the titanium plate is placed first, followed by screw implantation. However, the screw positions are not adjustable, resulting in a singular surgical approach and limited flexibility.
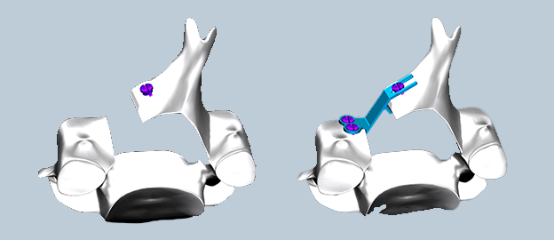
Leveraging extensive clinical experience and professional mechanical validation, Decon Medical has developed and designed the AQUA Series Lamina Fixation Plates. This system can accommodate both traditional surgical procedures and enable the Priority Screw Insertion Technique. This eliminates the risky steps of drilling and screw placement after performing laminoplasty and exposing the spinal cord.
IV. AQUA Lamina Fixation Plate System

Maximizes preservation of the musculoligamentous complex, maintaining and improving the cervical physiological curvature and kinematics.
Integrated lamina holders facilitate simple plate fixation; holders of various sizes accommodate diverse lamina morphologies. Integrated lateral supports ensure stable and secure plate fixation at the lateral masses.Both open-door plates and bone graft plates are available to accommodate individual anatomical variations.
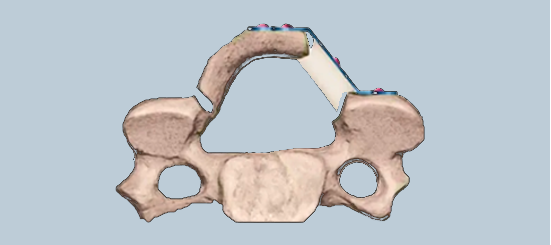
Innovative Product: U-shaped Titanium Plate
Innovative "U"-shaped bayonet design: Prioritizes screw placement on the intact lamina, eliminating the risky maneuvers of drilling and screw insertion after performing the laminotomy and spinal cord exposure.
Innovative "U"-shaped bayonet design: Features an oblong "U"-shaped slot that reduces constraints on screw positioning. This allows for fine adjustment of screw placement, significantly enhancing intraoperative flexibility and reducing procedural time.